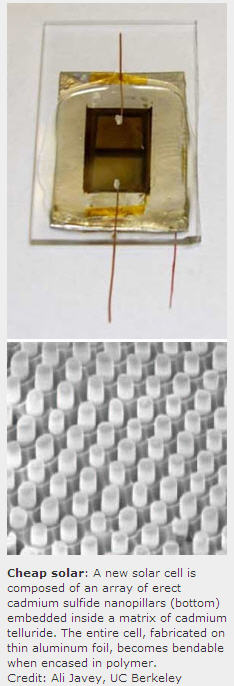
 Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have made a new kind of solar cell by growing an array of upright nanoscale pillars on aluminum foil. They make bendable solar cells by encapsulating the entire cell inside a transparent, rubbery polymer. The design, the researchers suggest, could lead to solar cells that cost less than conventional silicon photovoltaics.
Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have made a new kind of solar cell by growing an array of upright nanoscale pillars on aluminum foil. They make bendable solar cells by encapsulating the entire cell inside a transparent, rubbery polymer. The design, the researchers suggest, could lead to solar cells that cost less than conventional silicon photovoltaics.
The nanopillars allow the researchers to use cheaper, lower-quality materials than those used in conventional silicon and thin-film technologies.
So the cost would decrease 10 folds when it will be made on a big scale.
The solar cells are made of uniform 500-nanometer-high pillars of cadmium sulfide embedded in a thin film of cadmium telluride. Both materials are semiconductors used in thin-film solar cells.
In an online Nature Materials paper, it was shown that the cells have an efficiency of about 6 percent in transforming sunlight into electricity as compared to other nano pillars grown with expensive materials which have an efficiency of 2%.
In conventional cells, silicon absorbs light and creates free electrons, which need to get to the electrical circuit before they get trapped at defects or impurities in the material. This requires extremely pure, expensive crystalline silicon to achieve the most efficient photovoltaic devices.
The nanopillar design splits up silicon’s duties: the material surrounding the pillars absorbs light and creates electrons, and the pillars transport them to the electrical circuit. This increases efficiency in two ways. The closely packed pillars trap light between them, helping the surrounding material absorb more. The electrons also have a very short distance to travel through the pillars, so there are fewer chances of their getting trapped at defects. That means you can use low-quality, less expensive materials.
The researchers also intend to try other semiconductor materials for the pillars and surrounding material. The fabrication process is compatible with a wide range of semiconductors, and other combinations could increase the efficiency.