What do you think is common between these pictures: The rabbit-dolls or perhaps something that looks like a fancy kitchen ware – a dish?
I am sure you are still wondering what is it that you are looking at? But it definitely looks interesting enough to find out, doesn’t it? It is interesting, impressive and great fun!
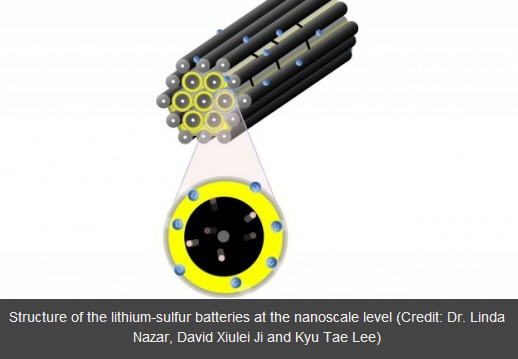
These are magical Violet Mirrors based on the RFID technology. RFID – stands for Radio-frequency identification. RFID can be applied to any object to use it as a tag, to be incorporated into any products to make them come alive. The RFID tag enables tracking the product through radio waves. In case you are wondering where this technology can be applied, then you should think of tracking and managing inventories at supermarkets, or any application of supply chain management in several enterprises.
If you understand the identification part of it, you would also immediately relate it to tracking, timing, scoring and implantation kind of usage. For example, an electronic toll collection booth would have an RFID tag put to its best use to improve efficiency in logging and tracking.
Other amusing uses that have been referred to is to use it as a learning package for youngsters, who can wave things in front of these RFID mirrors and understand the relation or usage of the same. For example, if you wave an umbrella in front of this magic mirror it would give you a weather forecast, or let you know when you took your last medication if you place your pills on it. It has to be connected to a computer to perform all these functions though.
The colorful RFID tags and stamps are slowly making place for their applications in our surroundings to make life more convenient, if it isn’t enough already. For now, inventory systems and identification are probably the best usage of this technology.
Main functions and features
Diameter 10 cm (4″). Height 1.4 cm (.55″)
Weight: 90g (3.2 oz)
USB 2.0 plug
ISO14443 Types A&B compliant RFID tag reader
Three dynamic color LEDs for feedback and information display
Speaker (buzzer)
Sleep mode sensor
Latest version of computer software downloaded from the website
Region free: works anywhere in the world, regardless of place of purchase
Requires permanent broadband Internet connection
Compatible with Mac OS X, Windows XP or Vista computer with USB port
Mirror can interact with other Violet objects such as Nabaztag:tag
Detects objects from a few centimeters
Detects up to four objects at the same time
Flipping Mir:ror puts it in sleep mode
When sitting idle on the desk Mir:ror displays light coded information for weather, stock quotes etc.
Works with Ztamps – the first consumer-oriented blank RFID tags that individuals can purchase and program to suit their own needs
Ztamps can be affixed to all kinds of everyday objects (mugs, keys, books, toys)
Ztamps can be re-used and reprogrammed by the user
Ztamps are not washable
Comes with: 1 Mir:ror (USB cable included), 3 blank user-programmable RFID Ztamps, 2 Nano:ztags programmable micro Rabbits, 1 Mirror:skin, 1 Quick start guide
- Diameter 10 cm (4″). Height 1.4 cm (.55″)
- Weight: 90g (3.2 oz)
- USB 2.0 plug
- ISO14443 Types A&B compliant RFID tag reader
- Three dynamic color LEDs for feedback and information display
- Speaker (buzzer)
- Sleep mode sensor
- Latest version of computer software downloaded from the website
- Region free: works anywhere in the world, regardless of place of purchase
- Requires permanent broadband Internet connection
- Compatible with Mac OS X, Windows XP or Vista computer with USB port
- Mirror can interact with other Violet objects such as Nabaztag:tag
- Detects objects from a few centimeters
- Detects up to four objects at the same time
- Flipping Mir:ror puts it in sleep mode
- When sitting idle on the desk Mir:ror displays light coded information for weather, stock quotes etc.
- Works with Ztamps – the first consumer-oriented blank RFID tags that individuals can purchase and program to suit their own needs
- Ztamps can be affixed to all kinds of everyday objects (mugs, keys, books, toys)
- Ztamps can be re-used and reprogrammed by the user
- Ztamps are not washable
- Comes with: 1 Mir:ror (USB cable included), 3 blank user-programmable RFID Ztamps, 2 Nano:ztags programmable micro Rabbits, 1 Mirror:skin, 1 Quick start guide
Source





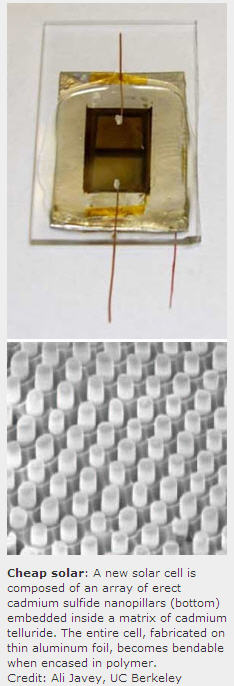 Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have made a new kind of solar cell by growing an array of upright nanoscale pillars on aluminum foil. They make bendable solar cells by encapsulating the entire cell inside a transparent, rubbery polymer. The design, the researchers suggest, could lead to solar cells that cost less than conventional silicon photovoltaics.
Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, have made a new kind of solar cell by growing an array of upright nanoscale pillars on aluminum foil. They make bendable solar cells by encapsulating the entire cell inside a transparent, rubbery polymer. The design, the researchers suggest, could lead to solar cells that cost less than conventional silicon photovoltaics.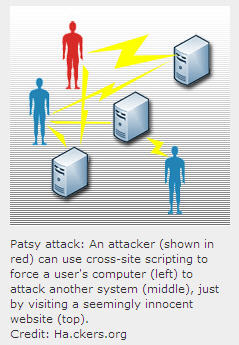 Sites that rely on user-created content can unwittingly be employed to attack their own users via JavaScript and other common forms of Web code. This security issue, known as cross-site scripting (XSS), can, for example, allow an attacker to access a victim’s account and steal personal data.
Sites that rely on user-created content can unwittingly be employed to attack their own users via JavaScript and other common forms of Web code. This security issue, known as cross-site scripting (XSS), can, for example, allow an attacker to access a victim’s account and steal personal data.